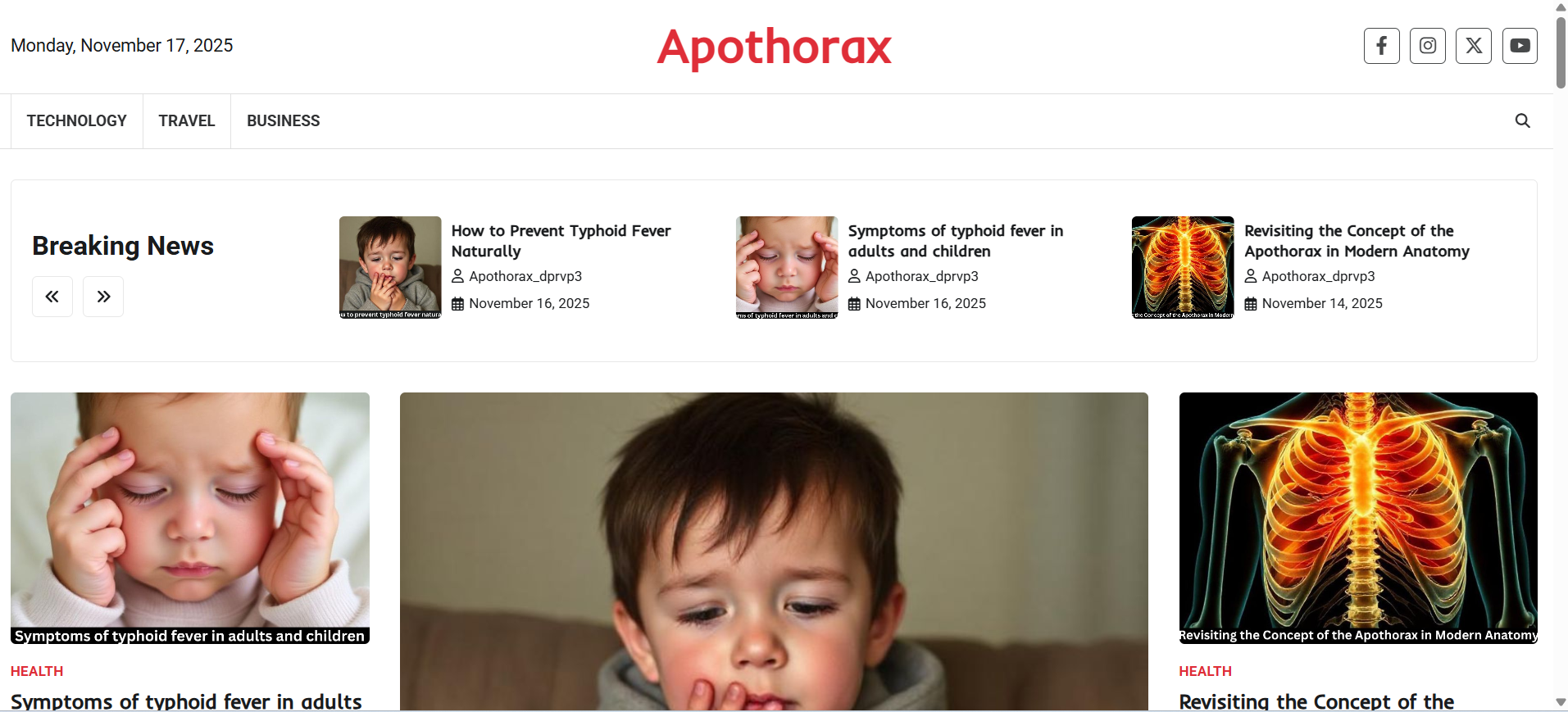
If you’re a biology or medical student, you’ve probably stumbled upon the term “apothorax” and thought, “Wait… what exactly is this?” Don’t worry—you’re in the same boat as thousands of others. The apothorax is one of those areas that sounds complicated but becomes surprisingly simple once explained properly.
Why Students Often Struggle with the Term “Apothorax”
The term isn’t used universally across all textbooks, which makes it confusing. Some books highlight it as a specific region of the thorax, while others simply skip the word altogether.
Importance of Understanding This Region in Anatomy
Despite the confusion, the apothorax includes some of the most vital organs in your body. Knowing this region well will help you understand breathing, circulation, and thoracic anatomy more clearly—especially for exams like NEET, board exams, or nursing entrance tests.
What Exactly Is the Apothorax?
Clear Definition
The apothorax is a subdivision of the thorax, located above the diaphragm and within the ribcage. It contains the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels.
Difference Between Thorax and Apothorax
- Thorax: Entire chest cavity
- Apothorax: A part of the thorax containing vital organ systems
Student-Friendly Explanation
Imagine the thorax as a large box. The apothorax is the upper portion of that box where the “power units” (heart and lungs) operate.
Where Is the Apothorax Located?
Superior and Inferior Boundaries
- Superior: Below the neck
- Inferior: Above the diaphragm
Relation to the Rib Cage
It sits snugly inside the ribcage.
How to Locate It on Your Own Body
Place your hand on your chest—right where your lungs and heart are. Congratulations, you’ve just located your apothorax.
What Organs Does the Apothorax Contain?
Heart
The central organ of circulation.
Major Functions
Pumps blood throughout the body, maintains oxygen supply, balances pressure.
Lungs
Your breathing engines.
Lobes and Gas Exchange
- Right lung: 3 lobes
- Left lung: 2 lobes
- Gas exchange happens in the alveoli.
Major Vessels
- Aorta: Main artery
- Pulmonary Trunk: Carries blood to lungs
- Vena Cava: Brings blood back to the heart
What Protects the Apothorax?
Ribcage
Acts like armor around the soft organs.
Intercostal Muscles
Help expand the chest during breathing.
Pleural Membranes
Reduce friction and protect lung tissues.
Why Is the Apothorax Important for Breathing?
Lung Expansion
Breathing begins with air rushing into the apothorax.
Diaphragm Function
The diaphragm contracts, pulling air into the lungs.
Inspiration vs Expiration Explained Simply
- Inhale: Chest expands
- Exhale: Chest relaxes
How Does the Apothorax Support Circulation?
Heart Positioning
The heart is positioned centrally to pump blood efficiently.
Role of Major Arteries and Veins
The apothorax is where the biggest vessels begin or end.
Common Student Questions and Their Answers
Is Apothorax a Real Anatomical Term?
Yes, though not used everywhere. Some books prefer “thoracic cavity.”
Why Do Some Textbooks Mention It and Others Don’t?
It depends on the curriculum or region; some simplify terminology.
Is It Important for Exams?
Absolutely—questions about thoracic divisions appear often.
How to Remember Its Boundaries Easily?
Think: Neck above, diaphragm below, ribs all around.
What Diagrams Should Students Practice?
Heart structure, lung lobes, rib arrangement, diaphragm.
What Medical Conditions Affect the Apothorax?
Pneumonia
Infection in the lungs.
Pleurisy
Inflammation of the pleural membranes.
Heart Diseases
Affects the central organ of the apothorax.
Trauma
Rib fractures, internal bleeding, organ injury.
How Is the Apothorax Viewed in Medical Imaging?
X-Ray
Shows lung size, fractures, fluid buildup.
CT Scan
Provides cross-sectional views of organs.
MRI
Shows soft tissues with high clarity.
Tips for Students Studying the Apothorax
Memory Tricks
Use mnemonics like “R.H.A.L.” — Ribs, Heart, Aorta, Lungs.
Diagram Practice
Draw the thoracic cavity repeatedly.
Exam Preparation Strategy
Focus on functions, structures, and diagrams.
Quick Recap of Key Points
- Apothorax is part of the thorax
- Contains heart, lungs, major vessels
- Protected by ribs, muscles, and pleura
- Essential for breathing and circulation
- Critical topic for biology exams
Conclusion
Understanding the apothorax doesn’t have to be confusing. Once you break it down—its location, organs, functions, and protections—it becomes one of the easiest regions to remember in human anatomy. Think of it as the “control center” of the human body, where the heart beats and the lungs breathe life into every cell. For students, mastering this region is a huge step toward stronger biology and medical knowledge.
FAQs
1. Is the apothorax and thorax the same?
No, the apothorax is a subsection of the thorax.
2. What organs lie within the apothorax?
The heart, lungs, aorta, vena cava, and pulmonary trunk.
3. Why do some books avoid the term “apothorax”?
Different educational boards use different terminology.
4. Is understanding the apothorax helpful for NEET?
Yes, it simplifies thoracic anatomy.
5. Can the apothorax be affected by infections?
Yes—pneumonia and pleurisy are common examples.